Pre- and post-install actions let you run custom PowerShell scripts or executables before and after an application installs. These actions can automate configuration checks, back up settings, create or remove shortcuts, change app settings, and add license or support files to ensure the app fits your environment.
Pre- and post-install actions were added in Right Click Tools Patching 5.10.2507.1103 (formerly Application Manager). In this post, we’ll show how to add install actions, why to use them, and a few real-world examples.
Enable Pre- and Post-Install Actions in Right Click Tools Patching
Pre- and post-install actions are configured at the deployment-process level. Before you configure actions, make sure the deployment process targets only one application. Consider deploying to a staging group first, in case any issues arise. PowerShell is powerful, so test thoroughly.
Go to Patching > Deployment Processes. Select the deployment process you want to modify. Click Manage Settings (…). Go to Advanced. Scroll to Install actions.
Toggle the Pre-install actions and Post-install actions sliders to enable them. Select Edit to add or change an action.

Choose an Action Type: Script vs. Executable
When you create actions, choose between two action types. Script actions run PowerShell either from the Use inline script field or from a network share using UNC path to script file. A script can be as simple as Get-Process -Name “ProcessName” | Stop-Process -Force to close a process before installation—or it can fully configure the application end-to-end.
Executable actions let you run an EXE before or after installation and pass parameters to it.
With either action type, you can copy extra files into the RecastAM subfolder, which sits next to the installer. Reference this subfolder in your scripts or parameters when you need those files.
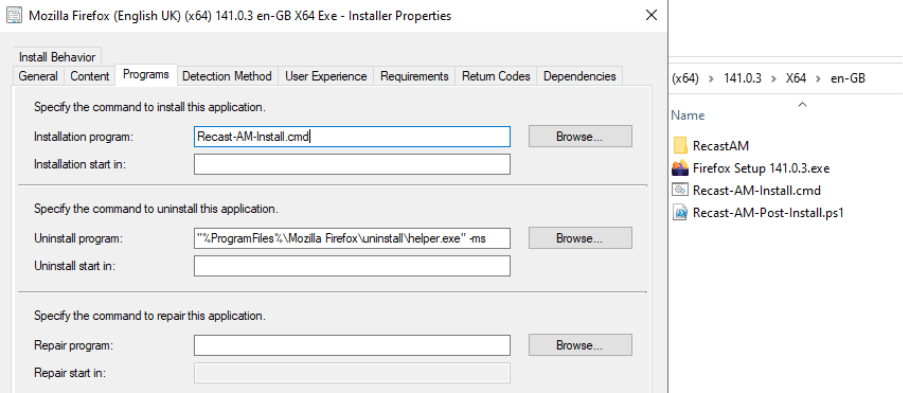
After you import an application that uses pre- or post-install actions into Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (MECM) or Intune, the installation program changes from the default. The installer is now a .cmd wrapper that runs the pre-/post-actions and then launches the original installer with default and custom parameters. The version-specific folder includes a RecastAM subfolder (for any extra files you copied) and a generated .ps1 file if you provided an inline script.
See our documentation for more details on pre- and post-install actions.
Example: Configure Mozilla Firefox with Post-Install Script (AutoConfig)
In this example, we’ll copy two configuration files into the 64-bit Mozilla Firefox installation directory to change default settings. To do this, you need to:
- Create two files: autoconfig.js and firefox.cfg. The first points Firefox to the configuration file; the second contains three preferences. The first preference sets and locks the default homepage to the Recast website. The other preferences prevent the “not default browser” prompt and the data-sharing notification.
- Autoconfig.js
pref("general.config.obscure_value", 0);
pref("general.config.filename", "firefox.cfg"); - Firefox.cfg
// Mozilla Firefox configuration
lockPref("browser.startup.homepage", "https://www.recastsoftware.com");
pref("browser.shell.checkDefaultBrowser", false);
pref("datareporting.policy.dataSubmissionPolicyBypassNotification", true); - Upload the files to a network folder accessible by the Recast Management Server (RMS).
- We recommend creating Scripts > Application subfolders in the same location where RMS downloads installation files.
- Edit the Firefox deployment process and create a post-install action.
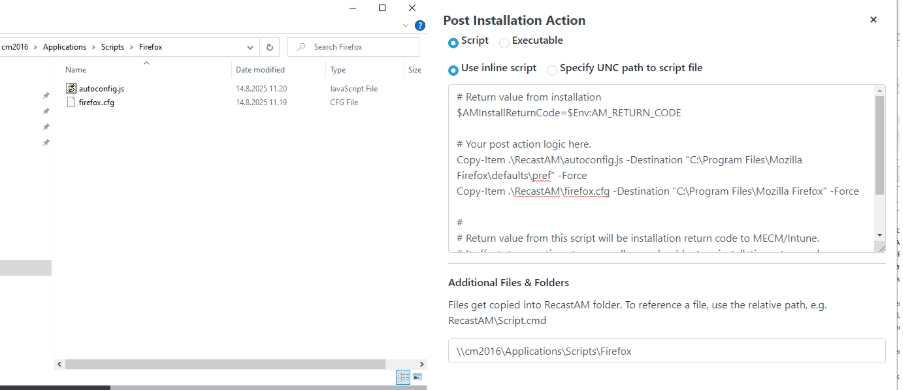
- Select Use inline script, then paste the following lines under the # Your post action logic here comment.
- The script will copy both files to correct location after the installation. Note: all files from the network folder are copied into the RecastAM subfolder, which is why the Copy-Item commands use the .RecastAM path.
Copy-Item .RecastAMautoconfig.js -Destination "C:Program FilesMozilla Firefoxdefaultspref" -Force
Copy-Item .RecastAMfirefox.cfg -Destination "C:Program FilesMozilla Firefox" -Force - In Additional Files & Folders, specify the network folder that contains the configuration files.
- Save the install actions and deployment process settings.
- Firefox preferences will be modified once the application is deployed to your environment.
You can find more information about Firefox AutoConfig files here.
Example: Assign TeamViewer Host with a Post-Install Delay
In this example, we’re deploying 64-bit TeamViewer Host and assigning the client to a specific TeamViewer account. You could use an Executable action, but TeamViewer assignment requires a short delay after installation completes.
- Modify the TeamViewer deployment process and add a post-install action.
- Select Use inline script, then paste the lines below under # Your post action logic here. Replace YOUR_ASSIGNMENT_ID with your assignment ID.
Start-Sleep -Seconds 30
Start-Process -FilePath "C:Program FilesTeamViewerTeamViewer.exe" -ArgumentList "assignment --id YOUR_ASSIGNMENT_ID" - Save the action and deployment process settings.
- TeamViewer Host is assigned to your account after the post-install action runs.
Why Pre- and Post-Install Actions Matter (Key Takeaways)
Pre- and post-install actions make application deployments smoother and more reliable. They help you move beyond “just installing software” by making sure your applications are configured correctly and are fully operational after setup. They automate what would otherwise be manual steps—making deployments faster, more reliable, and more end-user-friendly.
