Enterprise IT teams often struggle to keep Windows devices and apps up to date without disrupting users. Windows Autopatch is a cloud service from Microsoft designed to take over this burden and streamline update management across Windows, Microsoft 365 Apps, Edge, and Teams. In this post, we’ll explore what Autopatch is, how it works, and why it’s valuable for large organizations. We’ll also look at Autopatch’s architecture.
How Windows Autopatch Automates Updates
Instead of manually scheduling and pushing patches, Autopatch leverages Windows Update for Business (WUfB) and Intune to automate every step once devices are enrolled. Here’s how the process unfolds:
Enrollment and Policy Configuration
After you register devices with Autopatch, Microsoft’s cloud service automatically creates and applies the required Intune update ring policies, feature update deferral policies, and other profiles. Entra ID groups are used to segment devices into rings and enforce these policies without further admin intervention.
Phased Rollout via Update Rings
Autopatch divides your environment into deployment rings—Test, First, Fast, and Last—so that updates reach only a small pilot group at first. If no major issues arise, each successive ring receives the patch in turn, protecting the wider organization by catching bugs early.
Ongoing Monitoring and Control
Throughout the rollout, Autopatch continuously monitors device telemetry. If failure rates spike or compatibility problems emerge, it can automatically pause progression to the next ring. IT administrators always retain the ability to halt or roll back updates via Intune reporting and the Update Compliance dashboard.
Multi-Component Coverage
Windows Autopatch doesn’t stop at the OS. It also keeps Office apps on the Monthly Enterprise Channel, updates the Edge browser, and ensures Teams clients stay current—delivering consistent security and feature parity across your Microsoft software stack.
Windows Autopatch is a “set-and-forget” patching service: once enabled, it cycles devices through update waves in a safe, structured manner, freeing IT staff from routine manual tasks.
Enterprise Benefits of Windows Autopatch
Adopting Windows Autopatch can yield immediate and lasting advantages:
- Automated Patch Management
- By offloading monthly patch cycles to Autopatch, your team can focus on strategic projects instead of wrestling with thousands of individual updates.
- Improved Security and Compliance
- Autopatch’s SLAs (for example, targeting >95% of devices on the latest quality update) help you close security gaps quickly and demonstrate compliance through built-in reporting.
- Reduced Risk of Widespread Failures
- The phased ring approach catches problematic patches in small pilot groups, minimizing the chance of organization-wide disruptions.
- Consistency and Standardization
- A single, enforced update policy across all enrolled devices eliminates drift and simplifies audits.
- Enhanced End-User Productivity
- Users receive new features and performance improvements more quickly, and Autopatch respects maintenance windows and optimal reboot times to keep disruption low.
Autopatch Architecture and Update Rings
Windows Autopatch acts as an orchestration layer on top of Intune and Entra ID.
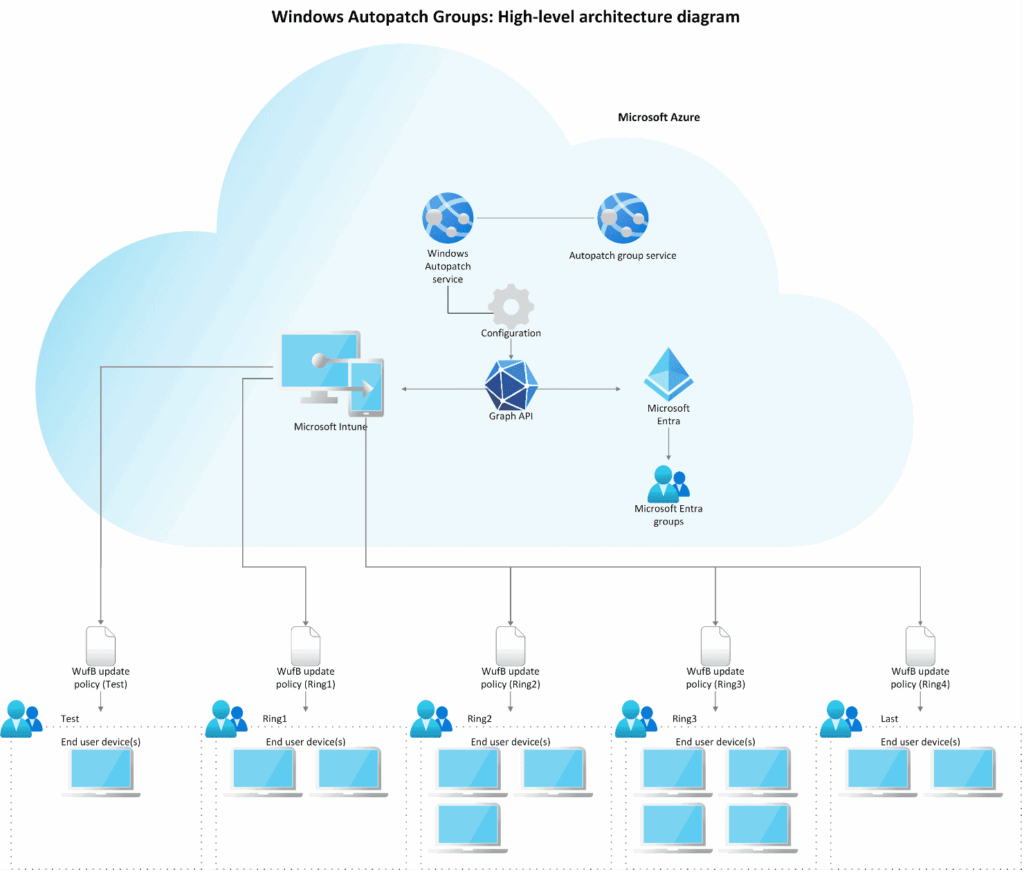
Intune Integration
Enabling Autopatch triggers the creation of best-practice update ring policies and Entra ID groups. Intune then applies these policies automatically to each ring.
Autopatch Groups and Percentage-Based Rings
By default, Autopatch provides a Test ring (small IT pilot group) and a Last ring (production). You can add intermediate rings—typically First ≈ 1%, Fast ≈ 9%, and Last ≈ 90%—and let Autopatch assign devices dynamically or map your own Entra ID groups. You can either let Autopatch dynamically assign devices to these percentage-based rings or map your own groups.
Policy Tiers and Deferral Settings
Each ring carries its own WUfB policy: immediate installs in Test, short deferrals in First, longer delays in Last. Urgent zero-day patches can bypass the normal schedule entirely, ensuring critical fixes reach all devices at once.
Automated Feedback Loop
After deploying to one ring, Autopatch analyzes success metrics before proceeding. High failure rates automatically pause rollouts, while smooth deployments trigger the next wave according to predefined intervals (e.g. +3 days, +7 days). Administrators always retain manual override controls in Intune.
Once set up, this cloud-managed ring architecture runs continuously, aligning with modern zero-trust and cloud-first management principles and providing a robust, hands-off update mechanism.
Conclusion: Automate Patch Management with Windows Autopatch
Windows Autopatch transforms the often daunting task of patch management into a predictable, automated process—allowing IT teams to focus on innovation rather than updates. With its phased rollout, multi-component coverage and built-in monitoring, Autopatch delivers both peace of mind and better protection for organizations of all sizes.
Learn more about third-party application management and patching, an important addition to fully securing your environment and application stack.


